Middle ear infections are common in babies and children age 2 and younger because their Eustachian tubes are shorter more horizontal straighter and more easily clogged than in adults. This is the most common type of ear discharge.
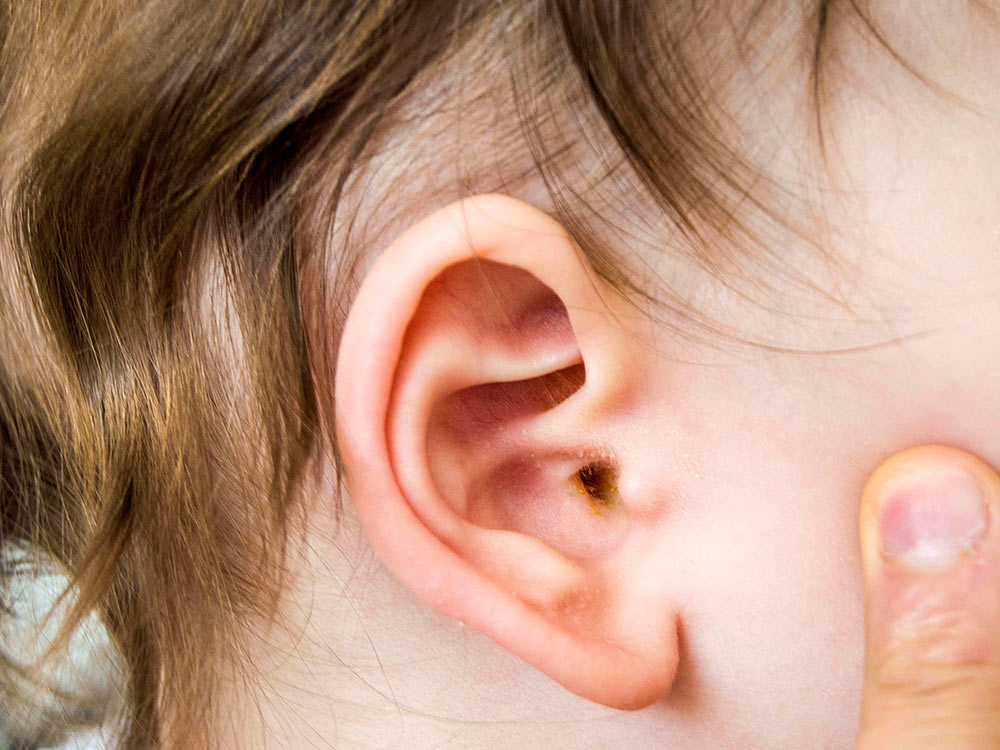
Ear Wax In Children What To Do About It Raising Children Network
If your child has symptoms of fluid in the ear it is best to take them to a pediatricians or an otolaryngologist ear nose throat specialist or ENT.
Fluid in ear toddler. If this tube called the eustachian tube gets blocked fluid builds up in the middle ear. Also described as weeping ear. Parts of the middle ear are infected and swollen and fluid is trapped behind the eardrum.
Whenever there is an ear discharge in your toddler it requires immediate medical attention. Use an eyedropper to put just a few drops of the solution into that ear and then have your child lie there for a few minutes while the liquid works its way into the wax build up. While anyone can get fluid in their ears children.
For some children the fluid goes away in a few weeks. When fluid in the ear doesnt drain properly out of the Eustachian tube it can build up in the middle ear just behind the eardrum. Pus or Cloudy Fluid.
Use a cotton ball or tissue to blot away any excess liquid or wax Have your child sit up. The fever your child often develops is due to the infection in the middle ear that his little body is fighting. Ear discharge also referred to as leaking ear is a common ear problem in children and adults alike.
Note that your tot could have excess fluid in the middle ear without that fluid becoming infected. The cause of ear discharge in children might be as simple as too much water in the ear or as complicated as a damage to a eardrum. Because fluid in the ear is often asymptomatic especially in children it often goes undiagnosed.
Lillian Beard author of Salt in Your Sock and Other Tried-And-True Home Remedies says salt is a way to remove fluid from a babys ear without the use of drops or medications. However this condition can occur any time whenever the auditory tube is impaired. In fact 90 out of 100 children will experience fluid in their ears at some point before the age of 5 or 6.
Acute otitis media AOM is the most common ear infection. This causes pain in the earcommonly called an earache. If your toddler is prone to recurring ear infections she may develop a build-up of thick fluid in the middle ear.
When the eardrum ruptures the discharge can be thick and yellow or even blood-stained fluid although all toddlers with eardrum rupture may not experience it. Have your toddler lie on their side with the blocked ear facing up. The drainage is from a torn eardrum.
This fluid buildup gives bacteria a place to grow which can cause an infection. Place 1 cup of coarse salt into the microwave for two to three minutes until it is warm but not hot. Your toddler may need to be referred to an ear nose and throat specialist.
And children have more frequent colds and other viral illnesses that can set them up for more fluid in the middle ear and more ear infections. Fluid can build up when a cold allergy or some other problem causes the small tube that carries fluid from the middle ear to the throat to swell and close. This can affect your toddlers hearing and may cause delays in speech development.
The ear discharge may have a bad smell because the draining fluid is the result of inflammation. Although anyone can get fluid in their ears children are much more susceptible to it due to the fact that their auditory tube is smaller and more horizontal than that of an adult. Your child might also have a fever.
The pain and temporary hearing loss your toddler sometimes experiences is due to the blocked fluid putting pressure on the eardrum. Fluid in ear also called serous otitis media or otitis media with effusion usually is the end result of an ear infection. The main cause is an ear infection.
Halaman
Baby & Child
Cari Blog Ini
Label
- 13th
- 14th
- 16th
- 2015
- 2016
- 2017
- abbott
- abortion
- about
- accuracy
- accurate
- ache
- achy
- acid
- acne
- activities
- activity
- acts
- acupuncture
- adhd
- adopt
- adopting
- adoption
- adulthood
- adults
- advanced
- advent
- advice
- after
- agencies
- agency
- alive
- allergic
- allergy
- along
- aloud
- alton
- amazon
- american
- ammonia
- amoxicillin
- anatomically
- andrea
- angel
- anger
- animal
- animals
- animated
- anna
- announcement
- announcements
- announcing
- answers
- anti
- antonio
- anxiety
- applesauce
- apps
- aquaphor
- arms
- arts
- aspirator
- aspirin
- atlanta
- attractions
- autism
- autistic
- average
- away
- babies
- baby
- babys
- babyshower
- babysit
- babysitting
- babywearing
- back
- backpack
- bags
- bahamas
- bake
- baked
- ball
- balloon
- balls
- banana
- band
- barometric
- basal
- base
- baseball
- bassinet
- bath
- bathing
- bathroom
- battle
- bauer
- bday
- beach
- beaches
- bean
- beautiful
- bedding
- beds
- beef
- beets
- before
- behavior
- behind
- being
- bell
- belly
- belt
- benadryl
- bench
- best
- better
- between
- beyond
- bible
- bike
- biography
- birth
- birthday
- bismol
- bite
- bites
- black
- blank
- blanket
- bleach
- bleeding
- blended
- block
- blog
- blood
- bloody
- blue
- blueberry
- board
- boat
- body
- book
- books
- booster
- boot
- boppy
- borax
- born
- bottle
- bottles
- bouncers
- boxes
- boyfriend
- boys
- brace
- bracelets
- bradley
- braids
- brazilian
- break
- breakthrough
- breast
- breastfeeding
- breastmilk
- breath
- breathe
- bright
- brisket
- britax
- broil
- brother
- brown
- brunch
- budget
- build
- bull
- bump
- bumped
- bumps
- bunk
- burping
- busbys
- busters
- butterfly
- buying
- buzz
- cabbage
- caff
- caffeine
- cake
- cakes
- calendar
- california
- call
- calls
- calorie
- camp
- camping
- camps
- cancun
- candy
- canker
- canopy
- cape
- capsule
- caput
- cardboard
- care
- carey
- carolina
- carolinas
- carpal
- carrier
- carriers
- carrot
- cars
- carseat
- casserole
- cast
- castaway
- casting
- catering
- cause
- cedars
- ceiling
- center
- centerpiece
- centerpieces
- cereal
- certificate
- cervix
- chair
- chairs
- challenge
- chamomile
- chance
- chances
- change
- changing
- chapter
- character
- chart
- cheap
- cheating
- check
- cheese
- cheesecake
- chef
- chest
- chicago
- chicco
- chicken
- child
- childbirth
- childhood
- children
- childrens
- childs
- chili
- chinese
- chip
- chocolate
- choice
- choking
- chops
- chore
- chores
- chowder
- christian
- christmas
- christopher
- cincode
- cinnamon
- circle
- claires
- clam
- claritin
- clarkson
- class
- classes
- classic
- clean
- cleaner
- clear
- climbers
- close
- cloth
- clothes
- clothing
- coast
- coat
- coed
- cold
- collections
- color
- coloring
- colors
- combo
- come
- coming
- commuter
- compact
- conceive
- conceived
- concussion
- connected
- cons
- constipated
- constipation
- consultant
- container
- containers
- control
- convertible
- cooker
- cookies
- cool
- cord
- corn
- cornstarch
- correct
- cost
- costa
- costume
- costumes
- cough
- coughing
- counter
- course
- cover
- cowboys
- crackers
- cradle
- cradles
- craft
- crafts
- craigslist
- cramping
- cramps
- crawls
- crayons
- cream
- creams
- creative
- creepy
- crew
- crib
- cribs
- cries
- crockpot
- cross
- cruise
- crying
- cuddling
- cupcakes
- curly
- curriculum
- curry
- curtains
- custody
- cute
- cyrus
- daddy
- dads
- daily
- dairy
- dallas
- danielle
- dating
- daughter
- daughters
- dave
- daycare
- dayquil
- days
- dayton
- deal
- deals
- decker
- decor
- decorate
- decoration
- decorations
- deep
- deliver
- delivery
- dentist
- depo
- depot
- desks
- destinations
- destiny
- determine
- detox
- development
- developmental
- device
- diabetes
- diaper
- diapering
- diapers
- diarrhea
- diego
- difference
- different
- dilated
- dilating
- dinner
- diono
- dippin
- discharge
- disney
- disneyland
- disneyworld
- distance
- division
- divorce
- does
- doesn
- dogs
- doll
- dollar
- dolls
- donate
- donation
- doors
- dosage
- dosing
- doterra
- double
- doug
- dough
- douls
- down
- downs
- dragon
- dragons
- dramamine
- drawing
- drawings
- drbrandt
- dream
- dress
- dressed
- dresses
- dressing
- drinks
- drive
- drowsiness
- drseuss
- duckie
- ducks
- dump
- during
- dwayne
- earache
- early
- ears
- easy
- eating
- eczema
- educational
- edward
- effects
- eggs
- elderberry
- elephant
- eliana
- elsa
- emergen
- emotional
- empty
- endocrinologist
- entertainers
- entertainment
- equate
- etsy
- evenflo
- evening
- event
- examples
- exercise
- exercises
- exhaust
- expect
- expensive
- experiment
- external
- extra
- eyelid
- eyes
- fabulous
- face
- facts
- failed
- faint
- fairy
- fake
- fall
- falls
- falmouth
- families
- family
- famous
- farm
- fashionable
- fashioned
- fast
- fathers
- favor
- favors
- feed
- feeder
- feeding
- feeling
- feet
- female
- fertility
- fever
- fiber
- fiction
- fidget
- fighting
- fine
- finger
- fingering
- firm
- first
- fisher
- fishing
- flay
- flipping
- float
- floaties
- floor
- florida
- flour
- fluid
- food
- foods
- football
- footprints
- ford
- forehead
- foreman
- formula
- foster
- free
- freezer
- friend
- friendly
- friends
- fritters
- from
- frozen
- full
- fumes
- funny
- gain
- gaines
- game
- games
- garage
- gardens
- gate
- gear
- gender
- generation
- genetic
- gerber
- gerbils
- gestational
- getting
- ghostbusters
- gift
- gifts
- ginger
- girlfriend
- girls
- givers
- giving
- glasses
- glazed
- glucose
- going
- goldilocks
- good
- gowns
- graco
- grade
- graham
- grandparents
- gravy
- green
- grieving
- grill
- grilled
- grinding
- grocery
- groin
- ground
- grow
- growing
- growth
- guard
- guide
- guitar
- gummies
- guns
- hair
- haircut
- hairstyle
- half
- halloween
- hand
- hands
- happy
- hard
- harry
- hasn
- hates
- have
- having
- hawaiian
- hazel
- head
- headache
- headbands
- healthy
- heart
- heartbeat
- heartburn
- heat
- heavy
- helicopter
- hello
- help
- hepatitis
- hero
- herpes
- high
- highback
- hips
- history
- hold
- home
- homemade
- honest
- hood
- hoodies
- hormones
- hospital
- hour
- hoverboards
- huggies
- humans
- hurt
- hurts
- husband
- hydrocephalus
- hydrocodone
- hydrocortisone
- ibuprofen
- icing
- idea
- ideas
- illness
- image
- implantation
- implants
- inch
- increase
- indian
- indiana
- indoor
- induce
- inducing
- inexpensive
- infant
- infants
- infection
- infertility
- infinite
- ingenuity
- ingrid
- insect
- insemination
- inspirational
- instructions
- instruments
- into
- invitation
- invitations
- ipack
- iron
- itch
- itchy
- jack
- jackets
- jennifer
- jesse
- jessica
- jessie
- jewelry
- joanna
- jobs
- jogging
- johnson
- johnsons
- joint
- jojoba
- jokes
- juice
- just
- jwoww
- kansas
- katherine
- kayla
- keep
- kelly
- keloids
- keyfit
- kids
- kill
- kindergarten
- kindergarteners
- kinesiology
- king
- kits
- kitty
- kmart
- knock
- know
- kristen
- kristoff
- labor
- lactation
- lactobacillus
- ladder
- ladies
- language
- languages
- large
- laser
- last
- latch
- late
- laugh
- laughing
- laws
- lead
- learn
- learning
- lego
- legroom
- legs
- lesson
- lessons
- letter
- letters
- lice
- life
- lifting
- ligation
- light
- lightyear
- like
- lind
- line
- lineless
- link
- lion
- lipstick
- liquid
- little
- locations
- locator
- locks
- loft
- london
- long
- look
- loose
- lose
- loss
- lotion
- lots
- louis
- love
- lower
- lubricant
- lullaby
- lump
- lunch
- lyrics
- magazine
- magnets
- make
- makeovers
- makes
- makeup
- making
- management
- manicure
- manners
- manuals
- many
- marble
- maria
- marinara
- mark
- markers
- marks
- marriage
- martha
- masks
- maternity
- math
- mattress
- mean
- meaning
- means
- medela
- medical
- medicine
- meds
- meijer
- member
- mental
- menu
- mermaid
- messages
- mexican
- mickey
- middle
- milestones
- milk
- mini
- minkoff
- minnie
- mint
- miscarriage
- miss
- missed
- missouri
- mistakes
- mittens
- mixed
- mixing
- moby
- model
- modeling
- modelling
- models
- moisture
- mommy
- moms
- money
- monitor
- monitors
- monkey
- monster
- monsters
- month
- months
- mood
- morning
- mosquito
- mosquitoes
- most
- mother
- mothers
- motor
- mount
- mouse
- mouth
- move
- movie
- movies
- much
- mucus
- muffins
- multivitamin
- murmur
- museum
- mushroom
- music
- musical
- nail
- name
- names
- nanny
- native
- natural
- naturally
- near
- neck
- need
- needs
- neelys
- negative
- neutral
- newborn
- newborns
- nice
- nicknames
- nicotine
- night
- ninja
- noodle
- north
- nose
- numb
- nurse
- nursery
- nurses
- nursing
- nuvaring
- oatmeal
- obstetrics
- octonaut
- offender
- often
- ohio
- oils
- ointment
- olaf
- older
- olds
- olive
- once
- onesie
- online
- orange
- oregon
- oreo
- organic
- organizer
- ornaments
- outdoor
- outfit
- outfits
- outside
- ovaries
- ovary
- oven
- over
- ovulate
- ovulation
- pack
- package
- packages
- page
- pages
- pain
- pains
- paint
- painting
- pajamas
- pally
- pamper
- pans
- panties
- pants
- paper
- parent
- parental
- parenthood
- parents
- parks
- parties
- partner
- parts
- party
- pasta
- patch
- payless
- pcos
- peace
- peach
- peanut
- pear
- peas
- pediatricians
- pedicure
- penny
- people
- peoples
- pepperidge
- pepto
- perego
- period
- personal
- peyton
- phil
- philosophy
- photo
- photography
- photos
- pickle
- pics
- picture
- pictures
- piercing
- piercings
- pierogies
- pill
- pillows
- pimple
- pineapple
- pink
- pipe
- pizza
- placenta
- places
- plan
- planned
- planner
- planning
- play
- playdough
- plays
- playset
- playsets
- please
- plug
- plus
- poehler
- points
- polish
- polly
- pooh
- pool
- pools
- pooped
- pooping
- pork
- portable
- portland
- poses
- position
- positions
- positive
- post
- postpartum
- potato
- potatoes
- potter
- potty
- predators
- prediction
- prednisone
- pregnancy
- pregnant
- prenatal
- preschool
- preschoolers
- present
- pressure
- prevent
- preventing
- price
- pricing
- printable
- problems
- process
- project
- projects
- prompts
- pros
- protect
- protein
- prunes
- ptosis
- puerto
- pump
- pumpkin
- pumpkins
- pupils
- puppy
- puree
- purple
- push
- quervains
- quesadilla
- questions
- quickly
- quiet
- quinceaneras
- quiz
- quotes
- race
- rachael
- rachel
- racing
- radian
- rails
- rapid
- rash
- rashes
- reaction
- read
- real
- realize
- rear
- reasons
- recall
- recalls
- receiving
- recipe
- recipes
- reclining
- recommended
- recovery
- recti
- reflux
- refrigerated
- refusing
- related
- relationship
- relationships
- remedies
- removal
- remove
- removed
- repellent
- requirements
- resorts
- response
- restaurants
- result
- results
- return
- reveal
- revealing
- reviews
- rica
- rice
- rico
- rings
- ringworm
- ripped
- rite
- roasted
- robe
- rock
- rocking
- roll
- rolls
- room
- rooms
- ross
- rubber
- rubiks
- rules
- runny
- sacroiliac
- safe
- safety
- sail
- salad
- salary
- sale
- saline
- saliva
- samantha
- sandwich
- sauce
- sauerkraut
- sbelts
- scan
- scanner
- scar
- scary
- schedule
- science
- scientist
- scooter
- search
- seat
- seater
- seats
- section
- seniors
- sensitivity
- seth
- sets
- setting
- seventh
- sexual
- shape
- sharp
- shaving
- shelf
- shirt
- shirts
- shoe
- shoes
- shortcake
- shot
- should
- shoulder
- shouldn
- show
- shower
- shrimp
- siblings
- sickness
- side
- siesta
- sign
- signal
- signs
- simple
- sing
- single
- singles
- sippy
- sister
- size
- sizing
- skellington
- skin
- sklice
- sleds
- sleep
- sleeper
- sleeping
- slides
- slings
- slow
- small
- smart
- smoking
- snapchat
- snot
- snow
- snowsuit
- soap
- soda
- sodium
- soft
- solly
- song
- songs
- soon
- sore
- sores
- sounds
- soup
- sources
- spaces
- special
- speech
- spicy
- spider
- spiral
- spit
- splotches
- spoons
- sports
- spot
- sprays
- spring
- sprinkle
- sprinklers
- spurts
- squash
- squats
- stage
- stages
- stains
- stand
- star
- starbucks
- stars
- start
- starting
- stationary
- stations
- stay
- staycation
- steak
- step
- sterilizer
- stew
- stewart
- still
- stocking
- stomach
- stool
- stools
- stop
- stopping
- stops
- storage
- store
- stories
- storybook
- stove
- straw
- strawberry
- strech
- strengthen
- strep
- stretch
- stroller
- strollers
- strong
- study
- stuffed
- stuffy
- style
- stylish
- styrofoam
- succedaneum
- sugar
- suits
- summer
- sunburn
- sunscreen
- super
- supper
- supplements
- supplies
- supply
- support
- surgery
- surrogacy
- swaddle
- sweaters
- sweats
- sweet
- sweetie
- swelling
- swim
- swimmer
- swimming
- swimsuit
- swimsuits
- swings
- switching
- swollen
- syllable
- symptom
- symptoms
- sync
- syndrome
- syrup
- systems
- table
- tags
- tailbone
- tails
- take
- taking
- talk
- talking
- tampa
- tampons
- tantrums
- tape
- target
- tatum
- teacher
- teachers
- teaching
- teds
- teenage
- teenager
- teenagers
- teens
- teeth
- teething
- tell
- temper
- temperature
- temple
- tendonitis
- tents
- term
- termination
- test
- tests
- texas
- thank
- thanksgiving
- that
- theme
- themed
- themes
- therapy
- there
- thermos
- thigh
- thighs
- thin
- things
- third
- this
- thomas
- thought
- thoughts
- three
- throat
- throw
- throws
- tick
- ticks
- tied
- tighten
- tightening
- time
- tingling
- tips
- toddler
- toddlers
- toilet
- tongue
- tool
- toothaches
- toppers
- tots
- toys
- track
- tracking
- trade
- traditional
- train
- training
- transitioning
- travel
- travelling
- treat
- treatment
- treats
- tree
- trees
- trend
- trends
- trick
- trimester
- trip
- trivia
- trouble
- trying
- tubal
- tubaligation
- tubes
- tummy
- tums
- tunnel
- turkey
- turn
- tutu
- twin
- twinkle
- twins
- tylenol
- types
- ultrasound
- ultrasounds
- under
- understands
- unicorn
- unplanned
- upper
- urine
- used
- uses
- vacation
- vacations
- valentine
- valentines
- vapor
- vaporub
- vasectomy
- vegetables
- versus
- vest
- vicks
- video
- videos
- violet
- vitamin
- vitamins
- vitex
- volunteering
- waist
- walgreen
- walker
- walkers
- wall
- wallpaper
- walmart
- want
- wanting
- warmer
- warmers
- washington
- watch
- water
- weaning
- wear
- wearing
- wedding
- wedge
- weed
- week
- weekend
- weekly
- weeks
- weight
- wesley
- what
- whats
- wheat
- wheeled
- wheels
- when
- where
- while
- white
- whole
- wife
- wild
- will
- winner
- winnie
- winter
- wipe
- wipes
- witch
- with
- without
- wolf
- woman
- womb
- women
- womens
- wood
- wooden
- wording
- words
- work
- worked
- working
- workouts
- worksheet
- world
- worth
- wrap
- wrapping
- wraps
- writing
- wrong
- wrongs
- year
- years
- yeast
- yelling
- yellow
- yogurt
- yolk
- young
- younger
- your
- yourself
- zeppelin
- zika
- zoloft
